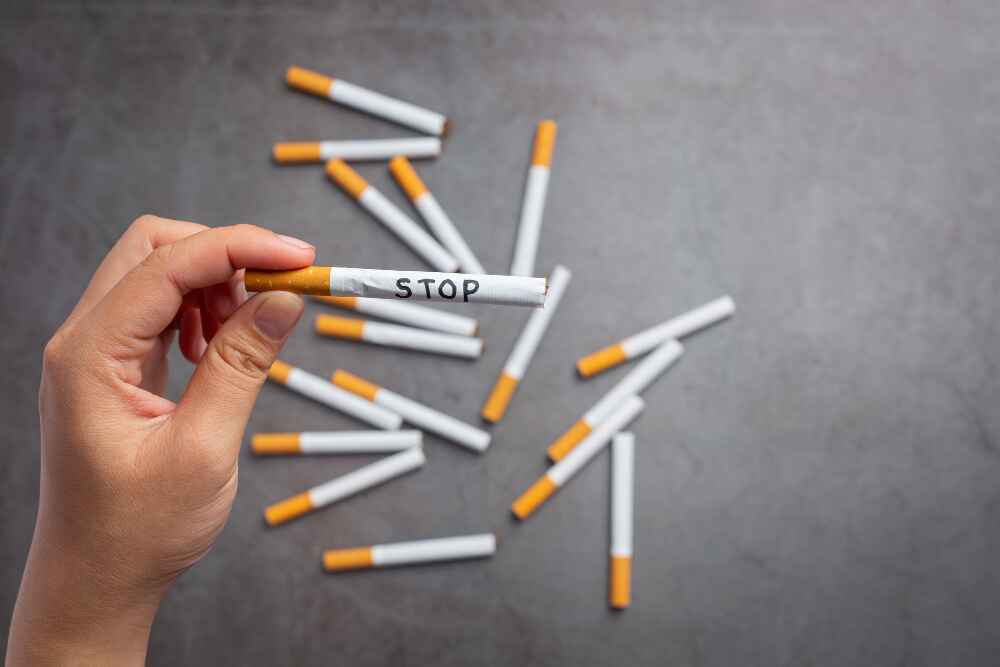
Smoking has been a pervasive habit for centuries, with millions worldwide indulging in it daily. However, beneath the illusion of tranquillity that a puff of smoke may bring, there lurks a sinister truth – smoking is a leading cause of cancer. The link between smoking and cancer is well-established.
Did you know that nearly 9 out of 10 lung cancer deaths are caused by smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke? This 5-minute read will shed light on the intricate web of mechanisms that connect smoking and cancer, and explore strategies for preventing this deadly outcome.
Do you know what causes cancer? Do you know the top 5 Reasons Why cancers are Increasing in Indian Youth?
The Connection Between Smoking and Cancer
Cancer, in general, is an uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells within our body which spreads like wildfire burning and destroying every tissue in its path. While there are 100 different types of cancer associated with several risk factors including genetic disposition and exposure to environmental toxins, smoking is the most significant cause. The good news, it’s preventable as well.
- 1. Toxin Are you aware that tobacco contains more than 7,000 chemicals? At least 250 of these are known to be harmful, with over 60 being classified as carcinogens. A carcinogen is any substance that has the potential to cause cancer.Some of these carcinogens include benzene, formaldehyde, arsenic, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). When these toxins are inhaled, they come in contact with the cells lining the respiratory tract and initiate cascading events.
- 2. Inflammation: Carcinogen irritates the delicate tissues of the respiratory tract causing inflammation. Inflammation, in turn, promotes the growth of damaged cells and inhibits the body’s immune system from effectively combating them.
- 3. Oxidative: Additionally, smoking causes oxidative stress leading to the production of harmful free radicals that can damage DNA and accelerate aging.
- 4. Mutation: Carcinogens bind to and alter the DNA within our cells, disrupting their normal functioning. Over time, it induces DNA damage and genetic mutations.
- 5. Impaired DNA Repair Mechanisms: Even though our bodies have amazing mechanisms to repair DNA damage and maintain cellular integrity, carcinogens can impair them. Thus, higher possibility of DNA mutations and uncontrolled division of accumulated cancerous cells.
- 6. Angiogenesis Promotion: Angiogenesis is a process by which new blood vessels are formed to deliver oxygen and nutrition to the body’s tissues. Smoking has been found to promote angiogenesis. While it’s a vital function for the growth, development and repair of wounds, sadly, it aids cancer cells as well to grow and spread.
Benefits of Smoking
Smoking is an ice break. People puff smoke on each other faces to socialise. It also helps people to relax and control hypertension by dropping blood pressure. It also reduces the possibility of obesity by reducing appetite and hunger and reduces mortality as well by causing:
- 1. Cancer
- 2. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- 3. Heart Disease
- 4. Stoke
- 5. Asthma
- 6. Ectopic pregnancy and reduced fertility
- 7. Diabetes
- 8. Blindness and Cataract
- 9. Age-related Macular Degeneration
All these and further impact babies with increased risk of health complications and even death.
The association between smoking and cancer is not limited to a single type. Smoking has been linked to numerous types of cancer, affecting various organs within the body, from the top:
- 1. Nose and sinuses
- 2. Mouth
- 3. Upper throat
- 4. Larynx
- 5. Oesophagus
- 6. Lungs
- 7. Liver
- 8. Stomach
- 9. Kidney
- 10. Pancreas
- 11. Bowel
- 12. Ovary
- 13. Bladder
- 14. Cervix
- 15. Blood (Leukaemia)
Preventing Smoking-Related Cancer
QUIT SMOKING is the most effective and efficient way to reduce the risk altogether. Even light, occasional or social smoking increases cancer risks significantly. Seek support from healthcare professionals, counselling services, or smoking cessation programs to help you kick the habit.
Avoid Secondhand Smoke: Even if you don’t smoke, inhaling smoke can increase your cancer risk. Avoid accompanying friends for smoke and environments where smoking is allowed.
Embrace a Healthy Lifestyle: Adopting a healthy lifestyle can help mitigate some of the damage caused by smoking. Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, engage in regular physical activity, and minimize alcohol consumption.
Regular Check-ups and Screenings: Regular medical check-ups and cancer screenings can detect cancer at an early, more treatable stage. Discuss your risk factors with your healthcare provider and follow their recommendations for screenings.
Supportive Therapies: Quitting can be strenuous for adapt smokers. Consider supportive therapies such as nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) or prescription medications, as recommended by healthcare providers.
Stay Informed: Continuously educate yourself about the risks of smoking and the benefits of quitting. Knowledge can be a powerful motivator in maintaining a smoke-free life.
The sooner one stops smoking, the lower the cancer risk. Everyone benefits from stopping, it’s never too late to quit smoking – even if you have smoked for years. Within 5 to 10 years of quitting, you reduce the risk of mouth, throat, voice box, and lung cancer to half. Furthermore, within 15 to 20 years, getting cancer will be lowered to that of a non-smoker.
Also read: Cancer Prevention: How to take steps towards reducing the risk of developing cancer?
Reach out to doctors, pharmacists, and stop-smoking services or visit Sum Ultimate to get support on how to stop smoking for good and control the withdrawal pangs.