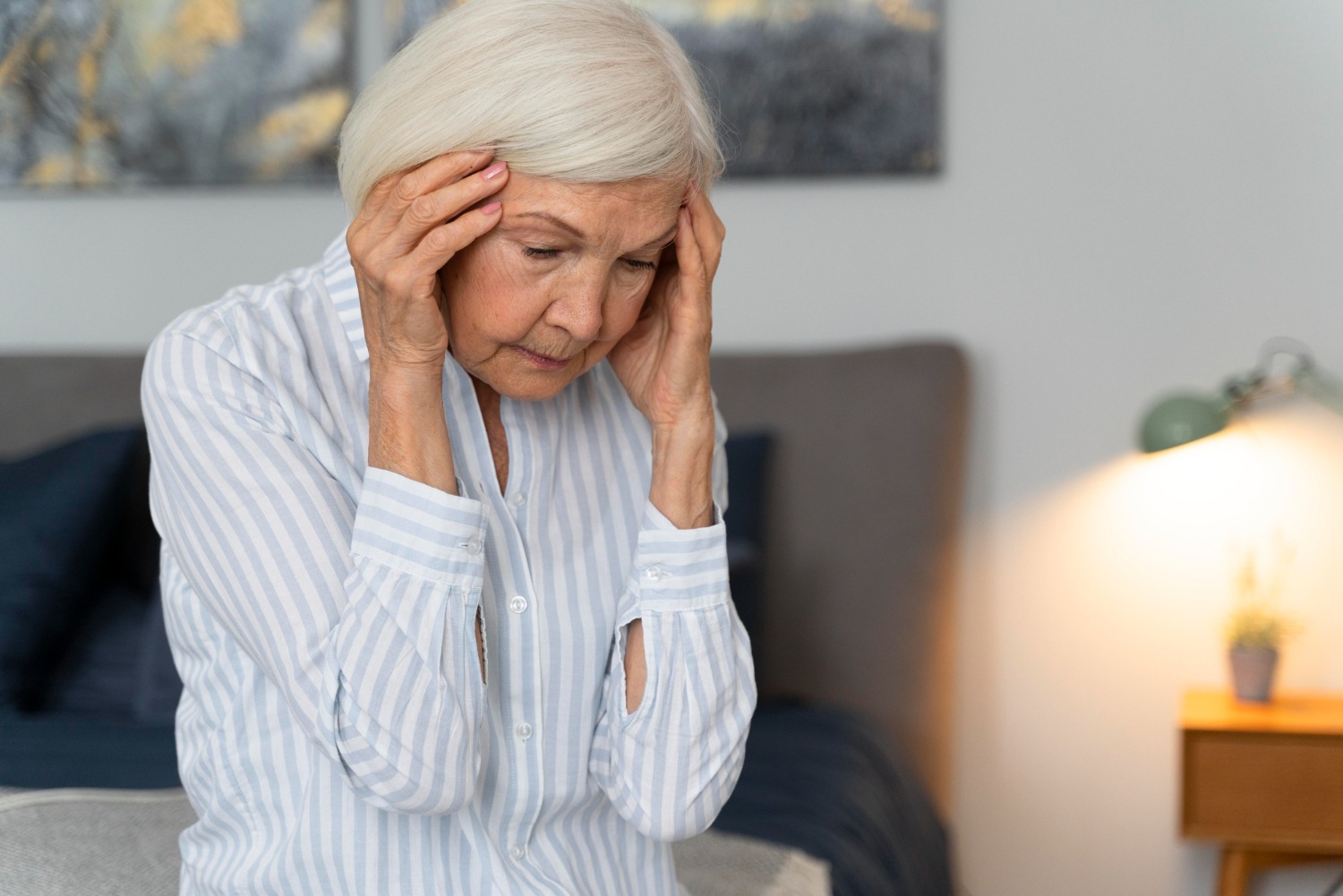
Imagine a world where memories slip through your fingers like grains of sand, where the once-familiar faces around you become strangers, and your own identity fades into the mist. Alzheimer’s disease is a neurological condition that leads to the gradual decline of brain cells, resulting in memory loss and cognitive impairment.
It’s a progressive and irreversible neurological condition that affects various aspects of an individual’s life, including:
- 1. Memory
- 2. Reasoning
- 3. Language
- 4. Coordination
- 5. Mood
- 6. Behaviour
The symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease typically manifest gradually, and they may vary in severity from person to person.
- ⦿ Memory Loss: Individuals in the early stages of Alzheimer’s often struggle to remember newly learned information, especially recent events, places, and names.
- ⦿ Language Difficulties: becomes increasingly challenging, leading to communication difficulties.
- ⦿ Misplacing Objects: It’s common for individuals with Alzheimer’s to experience frustration and anxiety.
- ⦿ Problems with Organisation and Problem-Solving: Routine Tasks can become daunting, and individuals may take longer to complete their daily routines.
It progresses through distinct stages, each presenting its own set of challenges:
Mild Stage: During this stage, individuals may struggle with the early symptoms as follows:
- 1. Difficult finding the right words to express thoughts
- 2. Misplace or lose objects more frequently than usual
- 3. Difficulty organising and problem-solving
- 4. Daily routines may take longer to complete
Moderate Stage: It is the longest phase of Alzheimer’s. Memory loss worsens, and individuals may have trouble recalling details of their lives, such as where they went to school or which day of the week it is. They might also struggle with:
- 1. Simple maths
- 2. Repeat stories, thoughts and events
- 3. Exhibit personality changes, including agitation, depression, and anxiety
- 4. Poor short-term memory
- 5. Sleep disturbances
- 6. Urinary or bowel incontinence
- 7. Difficulty recognizing the faces of family and friends is common.
Severe Stage: In the severe stage of Alzheimer’s, individuals require extensive care. They may experience the following:
- 1. Almost total memory loss
- 2. Unaware of their surroundings
- 3. Need complete assistance for basic activities like eating, sitting, and walking
- 4. Losses ability to communicate
This stage also leaves them vulnerable to infections and pneumonia, the most common reasons for the death of Alzheimer’s patients.
Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease
When to seek help? Friends and family may notice the symptoms before the person themselves. If in doubt, reach out to the best neurologists in Bhubaneswar. Someone with Alzheimer’s needs to get an accurate diagnosis early in the course of the disease is essential.
The obstacle in identifying early signs of Alzheimer’s is dismissing symptoms such as memory loss as a normal part of ageing or deviating them to other disorders such as depression.
You may consult with SUM Ultimate Medicare. Depending on the sign and severity of the condition suspected by the neurologist, the following diagnoses are carried out:
- 1. Physical and Neurological Examination: A thorough physical and neurological examination to rule out other potential causes of cognitive decline and provide important clues.
- 2. Cognitive Tests: Cognitive tests involve a series of questions, memory exercises, attentiveness assessments, and basic math tasks. While these tests can identify cognitive impairment, they alone cannot definitively diagnose Alzheimer’s disease.
- 3. Neuroimaging: Neuroimaging techniques such as CT scans, MRI scans, or PET (Positron Emission Tomography) scans can help visualise changes in the brain, including the presence of abnormal protein deposits associated with Alzheimer’s.
Alzheimer Treatment and Management
It’s important to note that there is currently no cure for Alzheimer’s disease, and the condition cannot be reversed or stopped. However, several Alzheimer’s treatment options and management strategies are available to help alleviate symptoms and improve the quality of life for both patients and their caregivers:
1. Medication:
While medication cannot cure Alzheimer’s, it can temporarily slow the progression of cognitive decline. However, these medications can have unpleasant and even dangerous side effects. It’s best not to lean on your understanding but rather follow the recommendations of neurologists.
2. Behavioural Interventions:
Individuals with Alzheimer’s get frustrated, anxious and threatened easily. Creating a safe and supportive environment can help such as:
- 1. Maintain a familiar environment: Avoid changing the layout or organisation of the living space to reduce confusion.
- 2. Monitor comfort: Pay attention to the individual’s physical and emotional needs.
- 3. Provide comfort objects: Familiar objects can provide a sense of security and familiarity.
- 4. Redirect attention: Distract individuals from stress or agitation.
- 5. Avoid confrontation: Minimize conflicts or confrontations, which can lead to increased anxiety.
Risk Factors and Prevention
While some risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease, such as age and genetics, cannot be controlled, there are several lifestyle factors and preventive measures that can help reduce the risk of developing the disease:
- ⦿ Staying mentally active: Engaging in activities like crossword puzzles, sudoku, chess, and learning to play a musical instrument can help keep the mind sharp.
- ⦿ Getting physically active: Regular exercise that increases blood flow and oxygen to the brain is essential. Protecting your head from injuries is also crucial.
- ⦿ Staying socially active: Maintaining social connections by talking with family and friends, participating in group activities, attending religious services, joining exercise classes, being part of a book club, or engaging in volunteer work can all help stimulate the brain.
- ⦿ Eating a healthy diet: Following a Mediterranean diet, limiting alcohol consumption, and quitting smoking can contribute to brain health.
Clinical research is ongoing to better understand the cause, develop new diagnoses, and treatments and discover preventive measures and possible cures. Reach out to the top neurologists of Bhubaneswar at SUM Ultimate Medicare, who in tandem with neurosurgeons, psychologists and psychiatrists, provide appropriate comprehensive Alzheimer’s treatment.